Monetary Damage of Reported Cybercrime in the US from 2001-2022
Growth in Cybercrime
Cybercrime is not just a threat to data and privacy; it also comes with a significant monetary cost. The monetary damage of reported cybercrime in the United States grew steadily from 2001-2017, and then accelerated starting in 2018. There was a year-over-year increase of around 50 percent from 2021 to 2022. Since this is just for reported cybercrime, the damages could be significantly higher due to unreported cybercrime incidents or unknown incidents. In the US, phishing and personal data breaches were among the most reported categories of cybercrime in 2022.
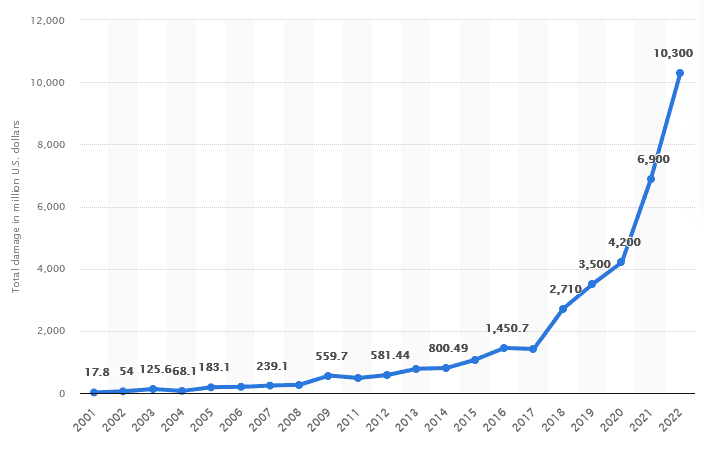
Source: Statista
Cybercrime Financial Costs
The monetary damage of cybercrime includes direct financial losses, such as stolen money, fraud, and extortion payments. For businesses, the average cost of a data breach is estimated to be around $3.86 million, according to the 2020 Cost of a Data Breach Report by IBM Security and Ponemon Institute.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable to cybercrime, as they often lack the resources and expertise to effectively protect against and respond to cyber threats. According to the Hiscox Cyber Readiness Report 2021, the average financial impact of a cyber incident on SMEs is $25,000, with 60% of SMEs experiencing a cyber incident in the past year.
Additional Cybercrime Costs
The cost of cybercrime extends beyond immediate financial losses, affecting businesses’ long-term viability and competitiveness. Indirect costs, such as lost productivity, reputational damage, and the cost of remediation and recovery, can also be substantial. Rebuilding trust with customers and partners after a cyber incident can be challenging and costly, leading to a loss of business opportunities and market share. Cybercrime also includes breaches on Operational Technology (OT) systems that can result in disruption, data extraction, or ransomware.
Cybercrime Mitigation
To mitigate the monetary cost of cybercrime, organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including employee training, regular security assessments, and the use of advanced security technologies. Proactive cybersecurity strategies can help reduce the risk of cyber incidents and minimize their financial impact, safeguarding businesses against the growing threat of cybercrime.
—
Blog Post Summary – All of our posts listed on one page back through 2019