Quantum Computing is Decades Faster than the Best Supercomputers
Quantum computers represent a profound leap in computational capabilities, fundamentally different from traditional supercomputers. While supercomputers rely on traditional binary logic, quantum computers exploit the principles of quantum mechanics, enabling them to compute certain problems exponentially faster.
Performance of Supercomputers vs Quantum Computers
In 2023 Google scientists reported in a study that it completed a computational task on a quantum computer that would take a classical supercomputer 47 years to complete. The Frontier supercomputer, which in 2023 was the most powerful computer in the world, would take a little over 47 years to process the same information that the Sycamore quantum computer completed in a little over 6 seconds. Google has since upgraded the Sycamore quantum computer, from 53 qubits to 70 qubits, increasing the processing capability by 241 million times.
While the new El Capitan supercomputer at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory currently ranks as the most powerful, it has incremental performance compared to Frontier, and still far below that of Sycamore.
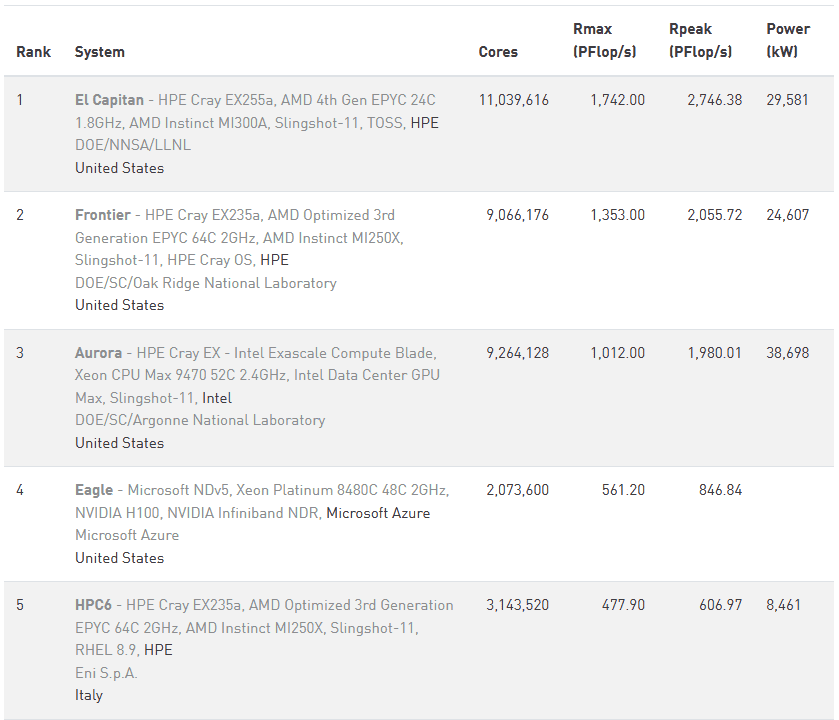
The list below shows the top 5 supercomputers:
Here is a list of the top 10 supercomputers and a nice graphical version as well.
Quantum Computing Impact on Encryption
The field of cryptography relies on the difficulty of solving certain problems, such as factoring large numbers or computing discrete logarithms. Classical computers struggle with these tasks due to their exponential complexity. Algorithms for factoring large integers are computationally expensive, making them the foundation of many encryption schemes like RSA. A classical supercomputer would take billions of years to factor a 2048-bit RSA key, but a sufficiently powerful quantum computer using Shor’s algorithm could perform the task in hours or even minutes.
RSA and ECC Vulnerability: RSA encryption, used widely in secure communications, depends on the infeasibility of factoring large numbers. Similarly, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) relies on the difficulty of solving elliptic curve discrete logarithms. Shor’s algorithm renders these problems trivial for quantum computers, effectively compromising RSA and ECC.
Symmetric Encryption: While symmetric encryption algorithms like AES are more resilient to quantum attacks, Grover’s algorithm can still halve their effective key strength. For instance, AES-256 would effectively become AES-128 under quantum attack, prompting the need for longer key lengths.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: In anticipation of quantum threats, researchers (including Veridify Security) are developing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms. These schemes rely on problems that remain hard even for quantum computers.
Quantum computers are poised to outpace classical supercomputers in solving problems that were previously thought to be infeasible. Their potential to break widely used encryption schemes underscores the need for proactive measures, such as developing and deploying quantum-resistant cryptography. When quantum computers mature, they could factorize 2048-bit RSA keys in minutes, compared to trillions of years for classical supercomputers. This speedup would render traditional encryption obsolete almost overnight, making the transition to quantum-safe cryptography urgent.
Quantum Computing Impact on Automation Controls
Devices that often have operational lifespans of decades – such as automation controls for buildings, manufacturing, and critical infrastructure – will be at risk from these future threats if they are not enabled now or capable of being upgraded later for post-quantum (PQ) protection with quantum-resistant encryption.
PQ Protection for Existing Automation Controls Enabling Next Steps
DOME, by Veridify Security, provides real-time protection for automation controls using a NIST-compliant Zero Trust framework. Devices are authenticated and all traffic is authenticated and encrypted, stopping attacks when intruders get past the firewall. To learn more you can watch a 4-minute demo about DOME.
—
Blog Post Summary – All of our recent posts listed on one page