Zero Trust Security for Building Management Systems in Data Centers

Data centers are an essential part of modern infrastructure, and downtime can result in disruption of services, reputational damage, and significant financial losses.
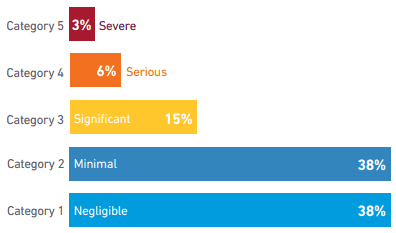
According to the Uptime Institute Annual Outage Analysis for 2024, power issues are consistently the most common cause of serious and severe data center outages, but 13-19% of data center failures were due to problems with cooling systems [1, 4]
There are several notable examples when data centers were taken offline due to environmental factors and colling issues including:
- Oracle and Google data centers taken down by UK heatwave [2]
- Twitter data center due to extreme heat [3]
The Cost of Data Center Outages
Data center outages are decreasing but the costs are rising [5].
- 53% data center of operators say their organization experienced an outage in the past three years, and this has been an improvement from 78% in 2020.
- Outage costs are estimated at under $100K (46%), $100K – $1M (33%), and >$1M (20%)
How Cyberattacks Can Manipulate Data Center Environments
1. Thermal Attacks via Workload Manipulation
Adversaries can exploit computational workloads to intentionally overheat servers, overwhelming cooling systems. Researchers demonstrated that running “power virus” programs or synchronized intensive tasks rapidly generates excess heat [6, 7]. This creates:
- Localized hotspots degrading server performance by 15-25% [6]
- Increased cooling energy consumption by 30-40% during attacks [7]
- Cascading failures when exhaust heat raises intake temperatures for adjacent racks [6]
2. BMS and Cooling System Compromise
Hackers targeting Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) systems gain control over:
- Change or override temperature set-points
- Cooling tower temperatures and fan speeds [8]
- Chilled water flow rates and humidity thresholds
- Emergency shutdown protocols for climate control
- Disabling alarms
Contemporary attacks could permanently damage hardware through sustained overheating.
3. Power System Sabotage
Exposed Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) interfaces enable:
- Forced transfers between grid and backup generators
- Battery depletion through false load signals
- Voltage fluctuations damaging sensitive equipment
Why Zero Trust Security is Essential for Data Center BMS
Environmental monitoring and building management systems (BMS) such as cooling, air flow, liquid leak detection, back-up power, and fire safety are key parts of data center infrastructure to keep the facility running with optimal performance and ready for potential disruption. These systems are increasingly connected to the internet and other networks, creating potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. Implementing a zero trust security model for BMS is essential for several reasons:
- Expanding attack surface: As data centers adopt more IoT and connected devices, the potential entry points for attackers multiply.
- Insider threats: Zero trust helps mitigate risks from both malicious insiders and compromised credentials by continuously verifying every access attempt.
- Complex environments: Data centers often have a mix of legacy systems, modern infrastructure, and third-party applications, making traditional perimeter-based security risky or ineffective.
- Regulatory compliance: Many data centers must adhere to strict regulations like PCI DSS, NERC CIP, or HIPAA.
Implementing Zero Trust for Data Center BMS
Implementing zero trust for building control systems requires a solution that can work across vendors and technologies, provide authentication for users and devices, and encrypt data across the network between devices. Veridify’s DOME platform was purpose-built for providing zero trust security to building controls and IoT devices. Important aspects include:
- Providing security for existing devices and system, regardless of device age or capability.
- Support for commonly used protocols including BACnet, Modbus, SNMP, and more.
- Automated certificate creation, distribution, and renewal.
- Device authentication – only authenticated devices can communication with each other.
- Data encryption with support for current and future quantum-resistant methods
References
[1] uptimeinstitute.com/resources/research-and-reports/annual-outage-analysis-2024
[2] techradar.com/news/oracle-and-google-data-centres-taken-down-by-uk-heatwave
[3] dataconomy.com/2022/09/14/twitter-data-center-offline/
[4] fossforce.com/2024/08/power-issues-cause-most-data-center-outages-followed-by-cooling/
[5] Uptime Institute Global Data Center Survey 2024
[6] ndss-symposium.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/ndss2018_06A-1_Gao_paper.pdf
[7] broadbandbreakfast.com/u-s-data-centers-could-face-security-threats-amid-ai-boom/
[8] cyble.com/blog/data-centers-facing-risk-of-cyberattacks/
—
Blog Post Summary – All of our recent posts listed on one page